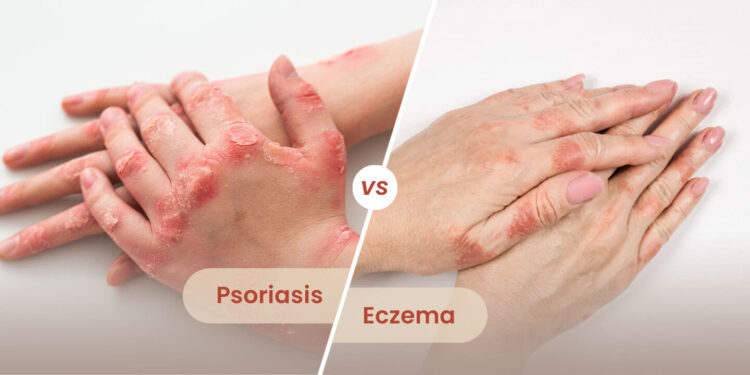
Psoriasis and eczema are two common skin conditions that can cause similar symptoms, such as dry, scaly skin, rashes, and itchiness. However, there are some key differences between the two conditions.
CALIFORNIA, UNITED STATES | NOW THEN DIGITAL — According to Jeffrey Millstein, MD, a physician at Penn Internal Medicine Woodbury Heights, the biggest distinction between eczema and psoriasis lies in their underlying causes.
Psoriasis is categorized as an autoimmune disease, where the immune system malfunctions, causing rapid skin cell growth. These excessive cells accumulate on the skin’s surface, forming a white scale.
Dr. Millstein explains that psoriasis typically induces milder itching and, in certain less common types, can result in a severe burning sensation. Conversely, eczema often triggers intensely itchy skin. In severe cases, individuals may scratch their skin vigorously, leading to bleeding.
For most psoriasis patients, ample exposure to natural ultraviolet B (UVB) light from sunlight can be beneficial. Dr. Millstein notes that UVB light has the ability to slow down the abnormal growth of skin cells, making it a useful medical treatment for psoriasis.
Psoriasis and Eczema: Understanding the Differences
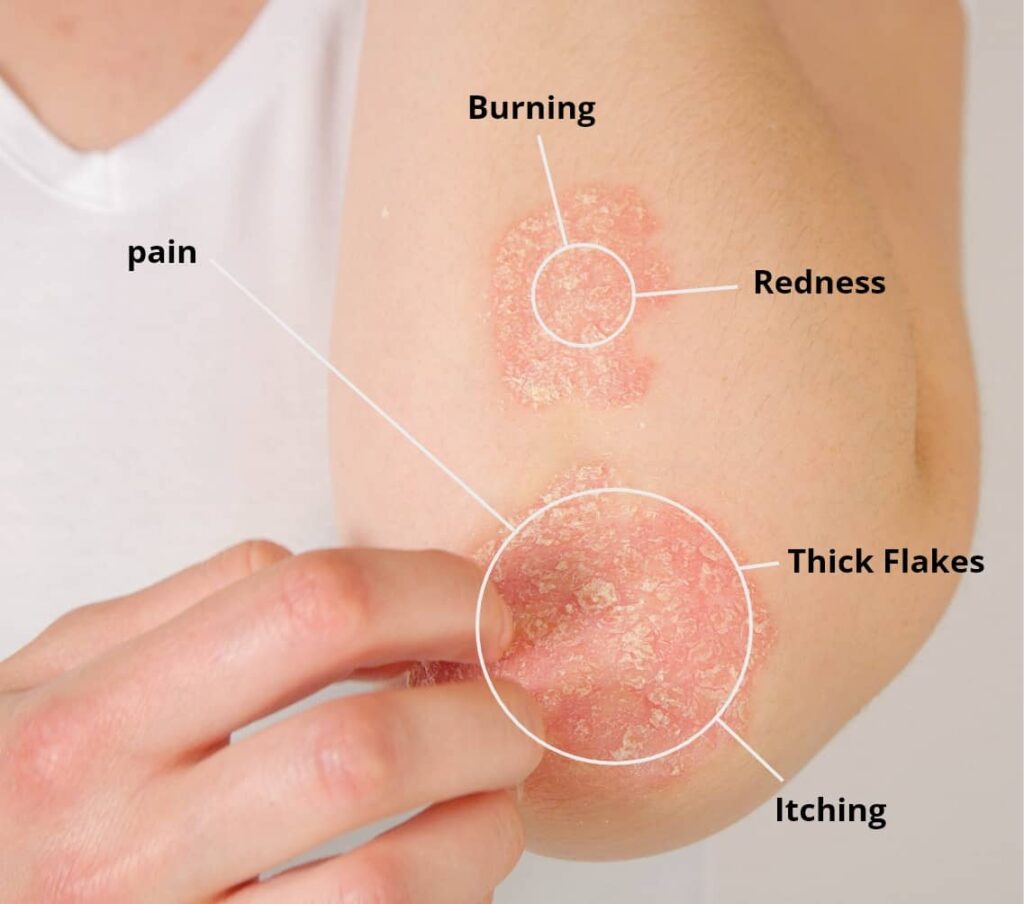
Symptoms
Eczema tends to cause more intense itching than psoriasis. When it becomes severe, some people scratch their skin so hard that it bleeds.
Eczema is usually characterized by poorly demarcated red, dry areas with fine scale, while psoriasis appears as red, silvery, and scaly raised patches of skin that are thicker and more inflamed than with eczema.
Psoriasis can also cause stinging or burning sensations, while eczema can cause swelling.
Causes
Psoriasis is an autoimmune disease that causes raised, scaly, silver-colored patches of skin, while eczema is a chronic skin condition that causes itchy, red patches of skin. Both conditions can be triggered by external factors, such as stress, infections, and certain medications.
Treatment
Treatment for psoriasis and eczema varies depending on the severity of the condition. Topical creams and ointments, such as corticosteroids, are often used to treat both conditions. In more severe cases, phototherapy or systemic medications may be necessary.
It is important to consult a dermatologist to get an accurate diagnosis and treatment plan for either condition. While both conditions can be managed, there is no cure for either.
In summary, while psoriasis and eczema can cause similar symptoms, there are some key differences between the two conditions. Psoriasis tends to cause milder itching and is characterized by raised, scaly, silver-colored patches of skin, while eczema causes more intense itching and is characterized by poorly demarcated red, dry areas with fine scale.
How Are Eczema and Psoriasis Diagnosed
Eczema and psoriasis are two common skin conditions that can cause inflammation, irritation, and skin discoloration. Although they share some similarities, there are also some differences in their symptoms and appearance.
Diagnosing Eczema
To diagnose eczema, a dermatologist carefully examines your skin during a physical exam and asks questions about your symptoms and medical history. They may also perform additional diagnostic tests, such as skin patch or skin prick tests, to see if certain allergic triggers cause a reaction on your skin.
Diagnosing Psoriasis
To diagnose psoriasis, a dermatologist examines your skin, nails, and scalp for signs of the condition and asks questions about your health and history.
They may also take a small sample of skin (biopsy) for examination under a microscope to determine the type of psoriasis and rule out other disorders.
Differences in Diagnosis
Eczema and psoriasis can look and feel very similar on the skin, but there are some differences in their appearance and symptoms. Eczema tends to develop in the folds of the skin, while psoriasis develops on outer surfaces, such as the elbows or scalp.
Eczema is usually characterized by poorly demarcated red, dry areas with fine scale, while psoriasis appears as red, well-circumscribed lesions (called plaques) with heaped-up, white scaling.
In some cases, a dermatologist may need to perform additional diagnostic tests, such as a patch test or skin biopsy, to distinguish between eczema and psoriasis.
If you suspect that you have eczema or psoriasis, it’s important to see a dermatologist for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment plan.
What Are the Most Common Triggers for Eczema and Psoriasis
Eczema and psoriasis are both skin conditions that can be triggered by a variety of factors. Here are some common triggers for each condition:
Eczema
Eczema triggers can vary from person to person, but some common triggers include:
– Irritants such as soaps, detergents, and shampoos
– Environmental factors or allergens such as cold and dry weather, dampness, house dust mites, pet fur, pollen, and mold
– Stress
– Hormonal changes
– Certain foods such as eggs, dairy, soy, and wheat
– Cigarette smoke
– Insects
– Overwashing
– Certain fragrances
– Metals like nickel
– Certain antibacterial topicals
– Paraphenylene-diamine (sometimes used in things like leather dyes and temporary tattoos)
– Formaldehyde (found in household disinfectants, some vaccines, glues, and adhesives)
– Isothiazolinone (an antibacterial that can be found in personal care products like baby wipes)
– Cocamidopropyl betaine (often used to thicken shampoos and lotions)
Psoriasis
Psoriasis triggers can also vary from person to person, but some common triggers include:
– Stress
– Injury to the skin such as a cut, scrape, insect bite, or sunburn
– Drinking excessive amounts of alcohol
– Smoking
– Hormonal changes, particularly in women
– Certain medications such as lithium, drugs taken to prevent malaria, and strong corticosteroids like prednisone
– Cold and dry weather
– Infections such as strep throat or tonsillitis
– Trauma to the skin
– Alcohol
– Certain medications
It’s important to note that triggers can vary from person to person, and what triggers one person’s eczema or psoriasis may not trigger another’s. If you have eczema or psoriasis, it’s a good idea to keep track of your symptoms and what triggers them so you can avoid those triggers in the future.
Additionally, it’s always a good idea to talk to your doctor or dermatologist about your condition and any concerns you may have.
What Are Some Natural Remedies to Alleviate Eczema and Psoriasis Symptoms
Eczema and psoriasis are chronic skin conditions that can be managed with a combination of medical treatments and natural remedies. Here are some natural remedies that may help alleviate symptoms:
Eczema
- Colloidal oatmeal: Add colloidal oatmeal to lukewarm bathwater and soak for 10 to 15 minutes to help soften rough skin and relieve itching. After your bath, pat your skin dry and apply a thick layer of hypoallergenic moisturizer that has a high oil content.
- Coconut oil: Apply coconut oil directly to the affected area to help moisturize and soothe the skin.
- Aloe vera: Apply creams containing 0.5% aloe vera up to three times per day to help reduce redness and scaling associated with eczema.
- Probiotics: Some people believe that probiotics can help improve eczema symptoms by restoring the balance of bacteria in the gut.
- Evening primrose oil: Some people believe that evening primrose oil can help reduce inflammation and itching associated with eczema.
- Witch hazel: Apply witch hazel to the affected area to help reduce inflammation and soothe the skin.
- Calendula cream: Apply calendula cream to the affected area to help reduce inflammation and promote healing.
Psoriasis
- Apple cider vinegar: Apply apple cider vinegar to the scalp several times a week to help relieve symptoms of psoriasis. Dilute it with a 1:1 ratio of water if it burns.
- Capsaicin: Capsaicin, a component of red peppers, has demonstrated the ability to fight inflammation. Apply creams containing capsaicin to the affected area to help reduce redness and scaling associated with psoriasis.
- Turmeric: Turmeric has anti-inflammatory properties that may help alleviate psoriasis symptoms. Add turmeric to your diet or take it as a supplement.
- Omega-3 fatty acids: Omega-3 fatty acids may help decrease inflammation in your body. This may be beneficial for psoriasis symptoms since systemic inflammation is the underlying cause of the itchy, discolored flakes. Omega-3s can be found in a variety of foods, including flaxseed oil, nuts, seeds, soy, and fatty fish.
- Dead Sea or Epsom salts: Put Dead Sea or Epsom salts into a tub with warm water and soak for about 15 minutes to help shed scales and soothe your skin.
- Tea tree oil: Apply creams containing tea tree oil to the affected area to help reduce inflammation and soothe the skin.
- Oregon grape: Apply creams containing Oregon grape to the affected area to help reduce inflammation and promote healing.
- Sun exposure: Spend some time in the sun to help fight psoriasis. Stick to 5 or 10 minutes a day, and use sunscreen on spots without psoriasis.
- “Season” your bath: Add Dead Sea or Epsom salts, oatmeal, or olive oil to your bath to help soothe your skin.
Remember to talk to your doctor before trying any new natural remedies, especially if you are taking prescription medications.
Editor’s Note: We would appreciate it if you could reach out to press@nowthendigital.com if you find any outdated or inaccurate content.