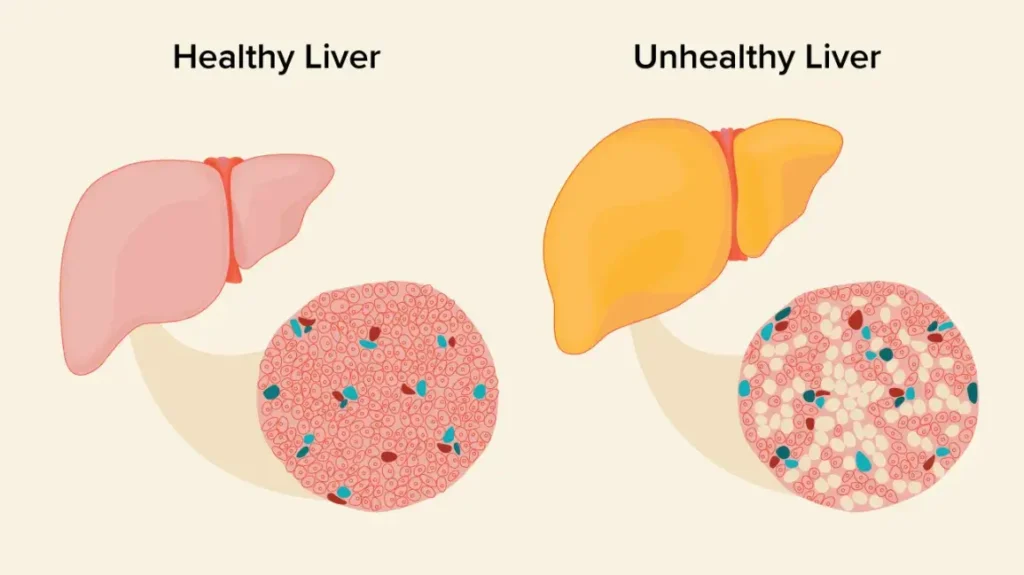
There are two types of fatty liver disease: alcohol-related fatty liver disease and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). People with non-alcoholic fatty liver may not exhibit any symptoms, but they remain at risk for liver damage.
CUPERTINO, CALIFORNIA | NOW THEN DIGITAL — Fatty liver disease occurs when your liver accumulates too much fat, or steatosis. This condition is more common among individuals with certain medical conditions like obesity, diabetes or high triglycerides levels.
- Fatty liver disease (also known as non-alcoholic fatty liver disease) is a liver disease that arises due to the accumulation of fat in the liver cells, and is a common cause of non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH), which is a leading cause of chronic liver.
- Obesity is the most frequent cause of NAFLD, though it can also be due to certain health conditions or medications. Other potential causes include diabetes mellitus, a high-fat diet and obesity-related inflammation (fibrosis).
- NAFLD can be diagnosed when there is an elevated level of fat (known as triglycerides) in the blood, or when tests reveal inflammation or tissue damage. When these levels exceed 150-199 milligrams per deciliter, it’s considered high.
- Some individuals are genetically predisposed to developing NAFLD. Research is underway to explore whether ABHD5 (a gene), may be linked to this condition. If your family has a history of NAFLD, be sure to discuss testing with your doctor.
Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is a condition that may be difficult to diagnose but blood tests and other tests can assist in doing so.
Patients are usually diagnosed with NAFLD in their 40s or later; however, given the current weight epidemic and the fact that it has become increasingly prevalent in younger adults, this diagnosis is often missed until a patient presents with elevated liver tests.
NAFLD is caused by a buildup of fat in the liver, which occurs when the body absorbs fat from the diet or takes fatty acids from the blood that are similar to cholesterol.
The risk for NAFLD increases as a person gets older; therefore, individuals who are overweight or obese should have regular screening.
If a person has NAFLD, they can have several different types of symptoms depending on the severity and extent of the disease.
The more serious symptom is Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis (NASH), which can lead to liver failure and eventually cirrhosis if the liver becomes severely damaged.
What are the signs of a fatty liver?

Your liver is an essential organ that processes food, filters out harmful substances in your blood stream, and keeps you healthy. The most common signs of a fatty liver are abdominal pain, fatigue, and an enlarged liver.
Other signs may include jaundice, itchy skin, and dark urine. If these signs are present along with other warning signs for this disorder, speak to your doctor about it.
Abdominal pain is caused by the fat pressing against the abdominal wall. Fatigue is caused by the liver not functioning properly. An enlarged liver is due to the fat buildup in the organ.
Jaundice is caused by the liver not being able to process bile properly. Itchy skin is caused when the liver has trouble breaking down toxins. Dark urine is caused by the liver not being able to process toxins, which can lead to them being excreted in the urine.
Additionally, you should get a blood test to check for liver enzyme levels and other tests to rule out any issues with your liver. You may also opt for an ultrasound or MRI scan to detect fatty deposits within the organ.
Fattening of the liver can be caused by either alcohol use (alcoholic fatty liver disease) or nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease is more prevalent than alcoholic fatty liver disease and more manageable when treating.
Fatty livers can lead to inflammation and damage within the cells of the liver, eventually leading to scarring (cirrhosis). This condition could eventually result in liver failure as well as increasing your risk for cancerous growths.
This inflammatory response can have serious repercussions for other health conditions, such as kidney or heart disease. It could even impair brain function and result in hepatic encephalopathy – an acute liver disorder.
Approximately 24-53 percent of individuals develop hepatic encephalopathy when their liver is bypassed by a portosystemic shunt.
Fatty liver is more common among those who are overweight or obese, as well as women postmenopausal. Furthermore, individuals with diabetes, high cholesterol, or high triglycerides also tend to develop the condition.
To prevent a fatty liver, the best approach is to limit alcohol consumption and consume foods low in saturated and trans fat. Additionally, eating plenty of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and healthy fats will help protect you against this condition.
Treating a fatty liver requires making changes in your diet and exercise regimen. Doing this will reduce the amount of fat stored in your liver, potentially helping to reverse its condition.
How can I reduce a fatty liver?

To reduce a fatty liver, make lifestyle modifications that promote its health. These may include abstaining from alcohol, altering your diet and controlling weight.
NAFLD affects about 25% of the world’s population and is the most common chronic liver disorder in the United States.
Fatigue of the liver, also known as fatty liver disease (AFLD), is an issue where fat deposits build up within the organ and may eventually lead to cirrhosis or liver failure if left untreated.
This condition comes in two primary forms – alcoholic fatty liver disease (AFLD) or non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD).
NAFLD (Nutrient-Deficit Hyperglycemia) is more common among those who are overweight, have diabetes, high cholesterol and/or hypertension.
Typically it begins with symptoms like fatigue, yellowing of the skin (jaundice) and abdominal pain; however it may also manifest without any warning signs or symptoms.
There are several dietary strategies that can help prevent or reduce fatty liver, such as eating low-fat and low-sodium foods. Eating foods high in vitamin E like red bell peppers, spinach, peanuts and nuts has also been found to improve this condition.
Eat plenty of vegetables, fruits and whole grains for a nutritious boost in energy levels. High fiber foods like vegetables, fruits and whole grains have a tendency to keep you fuller longer while helping regulate blood sugar levels.
Avoid high-fat meats, fried foods and saturated fats such as butter or ghee. Eating a nutritious diet that emphasizes vegetables, whole grains and lean proteins will help you lose weight, which in turn puts less strain on your liver.

Drinking water is essential for keeping the body hydrated, as well as being beneficial to the liver. Experts suggest consuming at least half an ounce of water for every pound of body weight daily.
Exercise can be beneficial, but should be done at a low intensity or for shorter durations of time. A low-fat, high-fiber diet with plenty of fruits and vegetables may also assist in managing a fatty liver.
Eating smaller meals more frequently can help your body digest food faster. A low-fat diet is especially important for decreasing the fat accumulation in your liver, which could be the source of inflammation.
Your doctor can prescribe medications that aid weight loss and decrease triglycerides, another type of fat in the blood. They may also be employed to regulate blood pressure which tends to be elevated for those with fatty livers.
What is the main cause of a fatty liver?
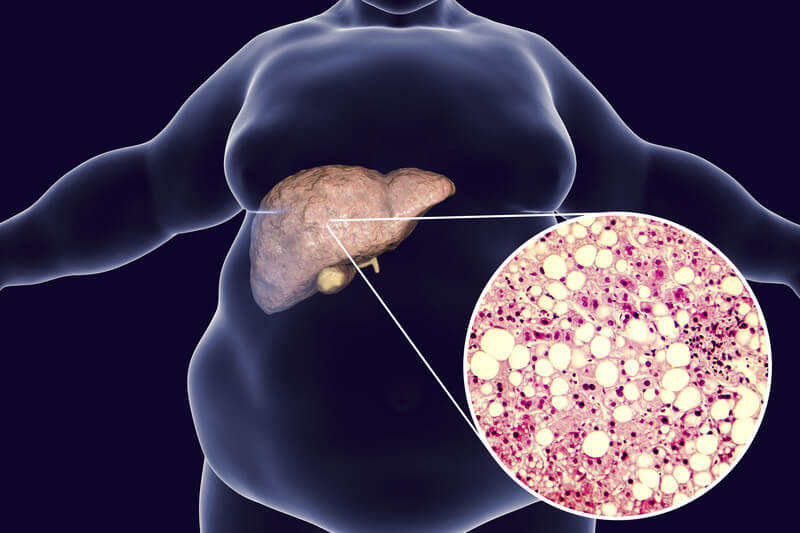
The liver is the largest organ in the body and functions to break down food nutrients, cleanse toxins from your system, eliminate waste products and store energy. It filters blood before it travels elsewhere in your body, as well as playing an important role in immunity by fighting infection.
Fat can build up in your liver if there is an abundance of it or it is not broken down properly by the organ, leading to steatosis. In certain individuals, this may lead to inflammation of the cells in your liver – known as steatohepatitis – which could eventually damage and render you ill.
Most people with fatty liver don’t experience any signs or symptoms, and may not even know they have it until testing reveals signs. These include abnormal liver function tests, abnormal blood count levels, imaging tests (such as ultrasound or computed tomography scan) that evaluate the shape of your liver.
Fatty liver can be caused by a number of things, such as obesity, an unhealthy diet that includes simple sugars and fatty foods, and alcohol use.
While some individuals are more at risk than others, this condition affects people of any age group.
Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease, or NAFLD for short, is a condition in which your liver struggles to breakdown fats as efficiently as it should.
NAFLD can progress into nonalcoholic steatohepatitis or NASH which causes inflammation and cell damage that could eventually result in scarring of your liver – known as cirrhosis.
Other risk factors for developing a fatty liver include being overweight or obese, having diabetes mellitus, and having obstructive sleep apnea (an obstruction in the airway that prevents breathing during sleep).
Furthermore, vaccination against hepatitis A, B, and influenza is recommended.
Treatment for fatty liver disease usually aims to improve your liver’s health by decreasing fat in your organ and aiding it in working better. To do this, avoid alcohol, maintain a healthy weight, and engage in regular physical activity.
Can a fatty liver be cured?

Fatty liver is a serious medical condition that can have dire consequences if left untreated. Without treatment, fatty liver may progress to cirrhosis of the liver, ultimately leading to liver failure and even death.
For patients with alcoholic fatty liver disease who continue to consume alcohol daily, the risk of developing fibrosis or cirrhosis after 10 years is 8–30%.
To determine whether you have a fatty liver, the best way to determine its presence is through a liver biopsy. This procedure involves inserting a needle into your skin and taking a small piece of liver tissue for examination under a microscope.
A pathologist will then be able to tell if you have simple NAFLD with no inflammation or nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) which could progress into cirrhosis of the liver if left untreated.
There is no cure for fatty liver, but it can be managed through lifestyle changes. The key to having a good quality of life and avoiding complications is managing your weight, abstaining from alcohol, and keeping cholesterol and triglyceride levels under control.
Patients diagnosed with NAFLD often see significant improvements when they change their diet and incorporate regular exercise into their routine.
A nutritious, well-balanced meal that includes plenty of fruits, vegetables, whole grains and low saturated fats into the meals can help regulate fatty liver.
A healthy, balanced diet is essential for preventing fibrosis and cirrhosis of the liver. People with fatty liver disease should try to limit their consumption of foods high in fructose as well as trans fats.
Maintaining a healthy weight, or losing excess pounds if you are overweight, is also important. Excess fat in the liver has been linked to an increased risk of cardiovascular disease, type 2 diabetes and certain cancers.
Treatment for fatty liver typically consists of lifestyle modifications and prescribed medications, and often leads to full recovery within several months. However, the length of recovery depends on the severity and stage of your disease as well as how well you adhere to recommended treatments and diet.
Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease, also known as NAFLD, is the most widespread form of this condition. It may be brought on by obesity or other factors like diabetes, autoimmune diseases or other health conditions.
Editor’s Note: We would appreciate it if you could let us know if any of our content is inaccurate or outdated at press@nowthendigital.com.
You’re reading nowthendigital.com — which breaks the news about Uganda, Kenya, Nigeria, South Africa and the rest of the world, day after day. Be sure to check out our homepage for all the latest news, and follow NOW THEN DIGITAL on YouTube, Google, Web Stories, Google News, Medium, Twitter, Reddit, Pinterest, Linktr, Buy Me a Coffee, and Flipboard to stay in the loop.

















