Physical examination alone cannot reliably detect shoulder injuries; your physician will likely request X-rays, possibly followed by an MRI or CT scan with an arthrogram (dye injected into the shoulder joint).
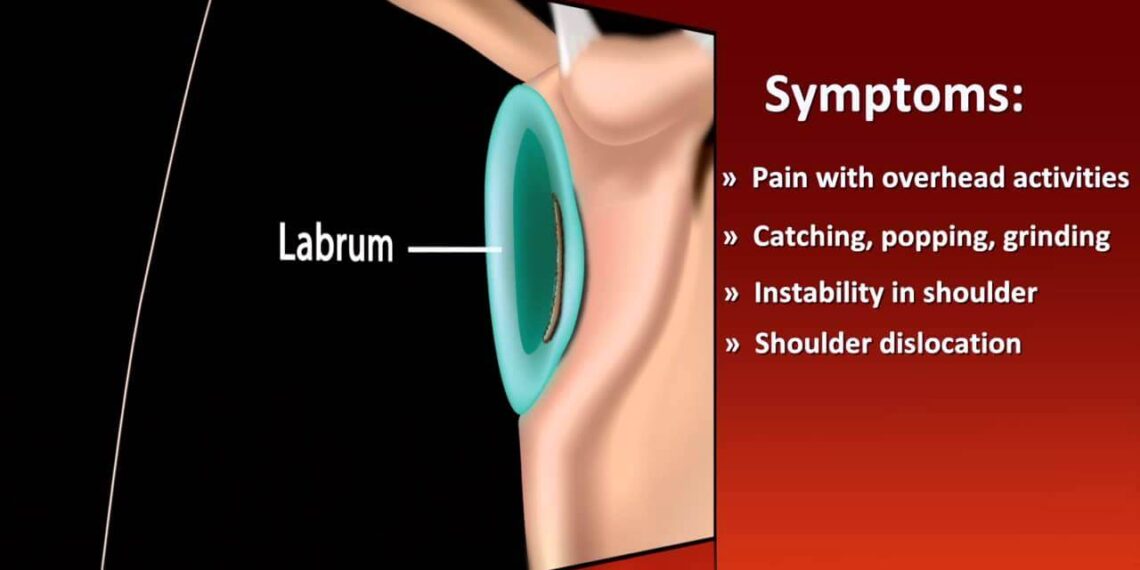
CUPERTINO, CALIFORNIA | NOW THEN DIGITAL — The shoulder labrum provides a protective rim to the shallow socket (shoulder blade, or scapula) where the upper arm bone (humerus) sits. It prevents its head from dislodging too easily from its place.
Your labrum is comprised of soft tissues that do not show up on an X-ray. Therefore, your doctor may order an MRI to better visualize it; sometimes dye may even be injected into your shoulder to increase visibility on an MRI scan.

Understanding the Shoulder Labrum Tear Test
Medical Tests or Diagnostic Procedures
Your shoulder consists of three bones: the scapula (shoulder blade), humerus (upper arm bone) and clavicle (collarbone). In between is an important cushion: the labrum. Without its support, however, you won’t have enough padding to ensure that the top of your upper arm bone rests snugly within its socket.
If this were to rupture, this cushion wouldn’t exist to provide cushioned protection to keep its place safely within the shoulder socket.
Physical exams are crucial to diagnosing shoulder pain. Your physician will ask about when and what caused the initial onset, what movements worsen symptoms and which movements cause inflammation.
Your doctor may order an MRI scan or CT-arthrogram test. These use magnetic waves to create images of your shoulder joint and special dye injection to reveal tears more clearly than regular X-rays; furthermore they are also better at diagnosing SLAP tears than regular x-rays although neither method is 100% accurate.
The shoulder labrum plays an essential role in keeping the shoulder joint stable. Its primary function is to deepen the socket so that the ball of the humerus stays centered within it – like a beach ball on a dinner plate – by attaching to bone structures or connecting via ligaments that connect bones directly. Additionally, it serves a structural function by keeping rotator cuffs secure within their sockets.
MRI
The shoulder is a ball-and-socket joint made up of thick bands of tissue which connect the bones in its socket. When this support becomes damaged, pain and weakness in the shoulder may occur, possibly as a result of injury or repetitive activities. A labrum tear may also result from such trauma.
Your physician can diagnose a shoulder labrum tear using advanced imaging tests such as MRI (magnetic resonance imaging). This technique utilizes magnetic waves to create images of the body’s bones and tissues – including those within your shoulder joint.
Before the exam begins, your physician will inject dye into your shoulder in order to easily spot damage during this exam.
Another possibility is a CT scan, which uses x-rays and computer technology to produce cross-sectional pictures of the shoulder.
For this test, it requires you to lie on a narrow table that slides into the scanner; your doctor may ask that you remain still during this exam and will likely ask you how long symptoms have existed as well as if any activities worsen your discomfort or increase it.
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scans are among the most reliable tests for diagnosing labrum tears. Magnetic resonance imaging provides your doctor with an opportunity to view your shoulder joint in detail, so they can look for signs of tear within.
Arthroscopy
Dignosing a labral tear can be challenging, particularly the more prevalent SLAP tear. This condition occurs when the shoulder’s rim of cartilage tears but remains attached to its socket in the glenoid. An MRI may help provide better images, and infusing dye into your shoulder joint will make its presence more evident on scans.
X-rays may also be used to evaluate the shoulder for problems with its articular cartilage, which protects bones in its joint. Cartilage allows bones to move smoothly against each other without experiencing frictional resistance.
When diagnosing and treating tears in the labrum, conservative care such as physical therapy to strengthen rotator cuff muscles and anti-inflammatory medication are typically first recommended.
If the pain persists after conservative measures have failed, arthroscopy may be used to make diagnosis and repair the labrum; this procedure typically requires either general or regional anesthesia and involves making a small incision into the shoulder joint to insert an arthroscope.
Physical Exam
A shoulder labrum tear may be difficult to diagnose as its symptoms often mimic other conditions, including pinched nerves.
A physician can conduct several physical tests in order to check for labral tears; one such reliable method is known as O’Brien test which involves positioning your arm into two different positions – if reduced pain in either position indicates labral tear pain is likely the source.
Another diagnostic test available is CAT scan, which employs dye to highlight damaged areas in the shoulder joint.
Your doctor can also perform arthroscopy, which provides direct visualization of labrum and cartilage within the shoulder to assess if there is a labral tear; however, this procedure can be invasive; should one be detected, the doctor can trim or repair it to alleviate symptoms; larger tears can be treated with rest or ice while smaller tears may require physical therapy treatment to stretch and reduce inflammation.
What Are the Treatment Options for a Shoulder Labrum Tear
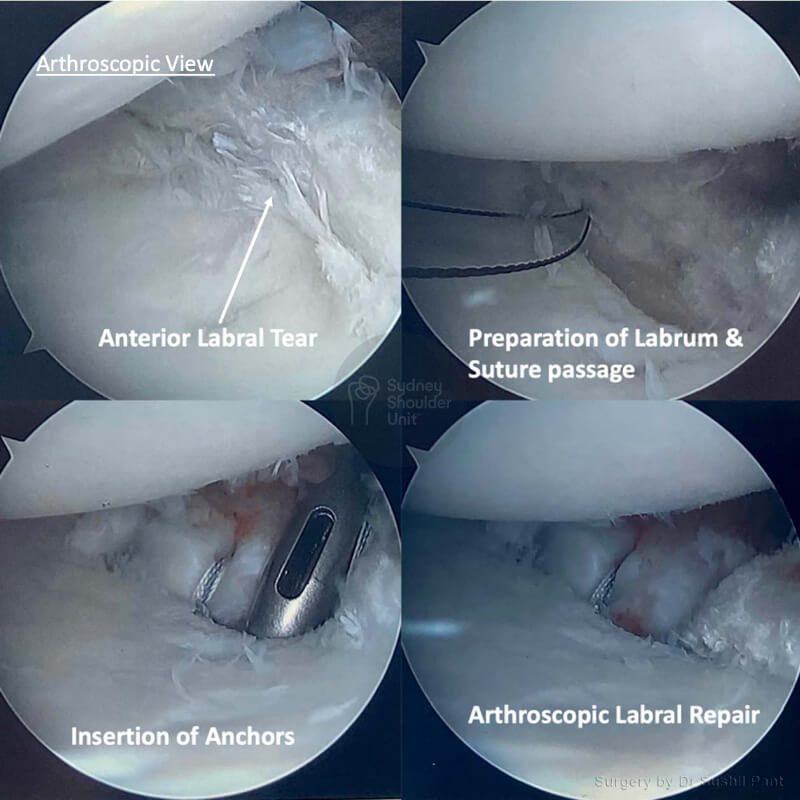
Treatment options for a shoulder labrum tear vary based on tear type, severity, and activity level. Nonsurgical options include rest, pain management, physical therapy, and injections. Arthroscopic surgery is the primary surgical approach.
Nonsurgical treatments involve:
- Resting the shoulder to allow labrum healing.
- Managing pain with anti-inflammatory medications like ibuprofen or naproxen, reducing swelling.
- Applying ice for 15 minutes, thrice daily, to reduce tissue swelling.
- Engaging in physical therapy for up to six weeks to strengthen the shoulder.
- Considering corticosteroid injections into the shoulder joint.
Arthroscopic surgery is the common surgical method, assessing the labrum and biceps tendon. The decision for these therapies depends on tear type, severity, and activity level, before surgery is discussed.
Recovering from a shoulder labrum tear treatment requires time. Surgical repair takes 9-12 months for complete healing. Post-surgery, physical therapy is often recommended to restore shoulder strength and range of motion.
It’s important to note that the connection between labrum tears and symptoms remains unclear, making it uncertain which tears require repair.
If a shoulder labrum tear is suspected, seeking medical attention for a proper diagnosis and treatment plan is vital.
What Are the Risks of Leaving a Shoulder Labrum Tear Untreated
Untreated shoulder labrum tears entail perilous risks and complications. The severity hinges on tear type, location, and activity level. Consider the risks:
- Chronic pain: A labral tear begets lingering pain and discomfort, especially during overhead endeavors or sports like basketball and tennis.
- Shoulder instability: The labrum bolsters the shoulder joint, fortifying its structure. A torn labrum jeopardizes stability, paving the way for dislocations and subluxations.
- Restricted mobility: Labrum injury impedes motor skills and mobility. If left untreated, the tear may morph into an enduring disability, forever altering the victim’s existence.
- Heightened osteoarthritis risk: Ignoring labrum damage substantially heightens chances of developing osteoarthritis in the affected joint.
- Escalated risk of further harm: A torn labrum renders the shoulder more susceptible to subsequent injuries, paving the way for grave shoulder complications.
Note that the correlation between labrum tears and symptoms remains elusive, hence the uncertainty surrounding which tears necessitate repair or can be left unaddressed. Nevertheless, if a shoulder labrum tear is suspected, prompt medical attention is crucial for an accurate diagnosis and treatment regimen.
Editor’s Note: If you come across any inaccurate or outdated content, kindly reach out to us at press@nowthendigital.com for immediate assistance.