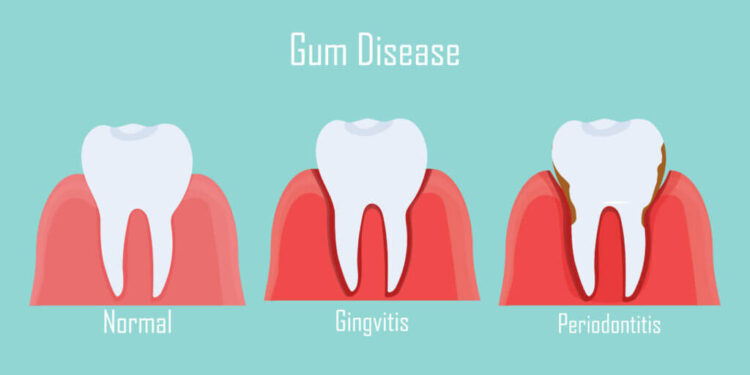
Practicing good oral hygiene, including brushing twice a day, daily flossing, and regular dental visits, can help prevent both gingivitis and periodontitis.
CUPERTINO, CALIFORNIA | NOW THEN DIGITAL — Gingivitis and periodontitis are two distinct forms of gum disease that vary in severity and symptoms. Here’s a breakdown of the key differences between the two:
The primary cause of both gingivitis and periodontitis is the buildup of plaque, a thin film composed mainly of bacteria that initially goes unnoticed. Plaque forms on the teeth and gums, causing irritation and inflammation of the gum tissue. Bacteria in the plaque consume sugars in the mouth, producing acids that can harm the teeth and gums.
Gingivitis
- The mildest form of gum disease.
- Caused by the accumulation of plaque, a bacterial film on the teeth and gums.
- Main symptom is bleeding gums.
- Additional symptoms may include redness, swelling, or tenderness of the gums.
- Usually reversible with proper oral hygiene and regular dental visits.
Periodontitis
- A more severe form of gum disease.
- Can lead to tooth loss as it damages the supporting tissues of the teeth.
- Symptoms include easily bleeding gums, redness, swelling, tenderness, and gum recession.
- Caused by plaque buildup that irritates the gums and causes inflammation.
- Good oral hygiene helps prevent gingivitis and slows down periodontitis progression.
- Early treatment is crucial to minimize damage and tooth loss.
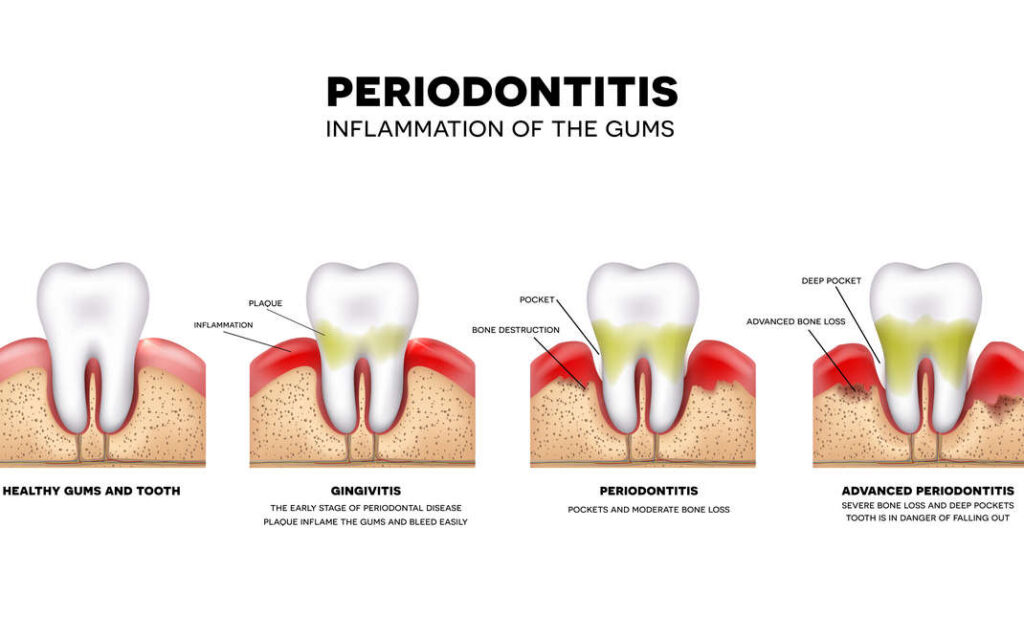
Causes of Gingivitis and Periodontitis
The primary cause of both conditions is the buildup of plaque, a thin bacterial film that initially goes unnoticed. Plaque forms on the teeth and gums, leading to gum tissue irritation and inflammation. Bacteria in the plaque consume sugars and produce acids that harm teeth and gums.
Other factors contributing to gingivitis and periodontitis risk include smoking or tobacco use, substance abuse, genetics, misaligned teeth, stress, nutrient deficiencies, puberty, pregnancy, hormone changes, certain medications, and metabolic diseases like diabetes.
Establishing good oral hygiene practices, such as brushing twice daily, daily flossing, and regular dental check-ups, can help prevent both conditions.
Diagnosing Gingivitis and Periodontitis
A dental examination by a dentist or periodontist is necessary to diagnose gingivitis and periodontitis. The diagnosis process involves the following steps:
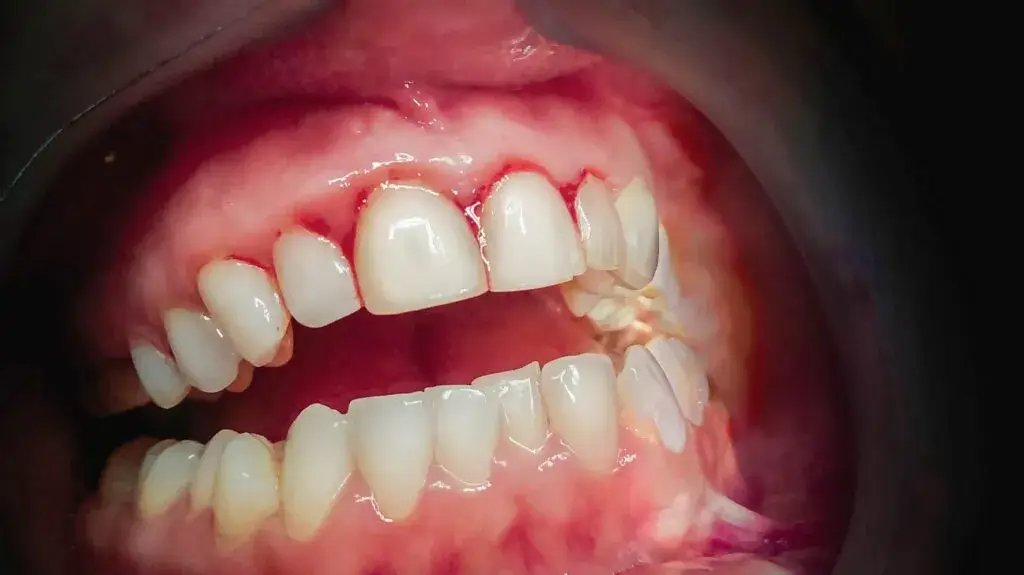
Diagnosing Gingivitis
- The dentist or periodontist examines the gums for signs of inflammation like redness, swelling, and bleeding.
- They may use a probe to measure the depth of the pockets between teeth and gums.
- X-rays may be taken to assess bone loss.
- Based on the examination results, the dentist or periodontist determines if the patient has gingivitis or another form of gum disease.
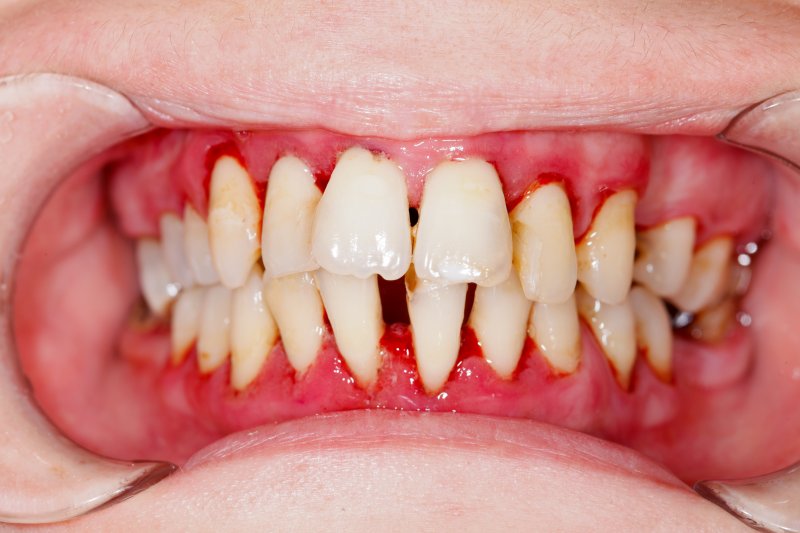
Diagnosing Periodontitis
- The dentist or periodontist examines the gums for signs of inflammation like redness, swelling, and bleeding.
- They may use a probe to measure the depth of the pockets between teeth and gums.
- X-rays may be taken to assess bone loss.
- Based on the examination results, the dentist or periodontist determines if the patient has periodontitis or another form of gum disease.
Treating Gingivitis and Periodontitis
Effective treatment options exist for both gingivitis and periodontitis. Here’s a look at the available treatments:
Treating Gingivitis
- Gingivitis can often be treated by adopting good oral hygiene practices, including brushing twice daily, daily flossing, and using antiseptic mouthwash.
- Professional dental cleaning may be recommended to remove plaque and tartar.
- In some cases, antibiotics may be prescribed to address underlying infections.
- Maintaining good oral hygiene helps prevent gingivitis development or recurrence.
Treating Periodontitis
- Treatment for periodontitis typically involves a deep cleaning procedure called scaling and root planing.
- Scaling removes plaque and tartar from tooth surfaces and below the gum line.
- Root planing smooths tooth root surfaces to facilitate gum reattachment.
- Antibiotics may be prescribed to address underlying infections.
- Advanced cases may require surgical interventions like tissue removal or grafting.
- Sustaining good oral hygiene helps prevent periodontitis development or recurrence.
Costs Associated with Periodontitis Treatment
The cost of periodontitis treatment varies based on factors like the recommended treatment type, gum disease severity, and location of the dental practice.
Treatment costs can range from $1,700 to $8,000 for periodontal disease treatment and average $200.00-$300.00 per tooth for extractions at Ellicott City Dentistry. Costs in Mesquite, TX, range from $50 to $75 for regular dental cleaning, $140 to $210 for scaling and root planing, and $1,500 to $3,500 for gum grafting.
In New York City, periodontal therapy costs about $350 per quadrant, while scaling and root planing costs $100 to $450 per quadrant or up to $4,000 for the entire mouth. Dental insurance typically covers periodontal disease treatment, but a co-pay of 20% may apply. Consultation with a dentist will provide more precise cost estimates for individual cases.
In summary, the treatment costs for periodontitis vary based on treatment type, gum disease severity, and location. It is advisable to consult with a dentist to obtain accurate cost estimates for periodontitis treatment.
Editor’s Note: If you find any of our content to be inaccurate or outdated, please contact us at press@nowthendigital.com