Managing periodontitis at home involves maintaining good oral hygiene practices, making lifestyle changes, and trying home remedies to alleviate symptoms.
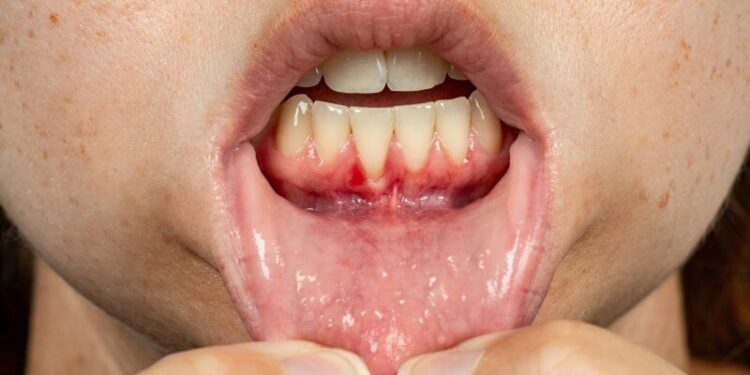
CUPERTINO, CALIFORNIA | NOW THEN DIGITAL — Periodontitis, commonly referred to as gum disease, poses a significant risk to oral health. This profound infection, stemming from bacterial buildup on teeth and gums, wreaks havoc on delicate tissues, potentially leading to tooth loss and persistent discomfort.
With over 1 billion global cases, comprehending the comprehensive nature of this condition is essential for informed decision-making.

Periodontitis, an inflammation that progressively worsens, manifests through a series of troubling symptoms. From inflamed and swollen gums to discolored plaque and bleeding during oral care routines, the signs of periodontitis demand attention. Halitosis (bad breath), pain while eating or chewing, tooth sensitivity, receding gums, and even tooth mobility or gaps further characterize this condition.
Early diagnosis and prompt treatment are critical. “Regular visits to oral health professionals, ideally twice a year, play a vital role as patients may find it challenging to identify the disease independently,” emphasizes Chris Richardson, D.M.D., an esteemed dentist and President of the American Academy of Periodontology based in Richmond, Virginia.
Disturbingly, severe periodontal diseases afflict approximately 19% of the global adult population, surpassing the staggering milestone of 1 billion cases. The World Health Organization (WHO) attributes poor oral hygiene as the primary instigator of periodontitis. Inadequate dental care fosters the accumulation of plaque and tartar, providing a breeding ground for harmful bacteria.
These pathogens infiltrate gum tissues, triggering inflammation, infection, and the eventual onset of periodontal disease.
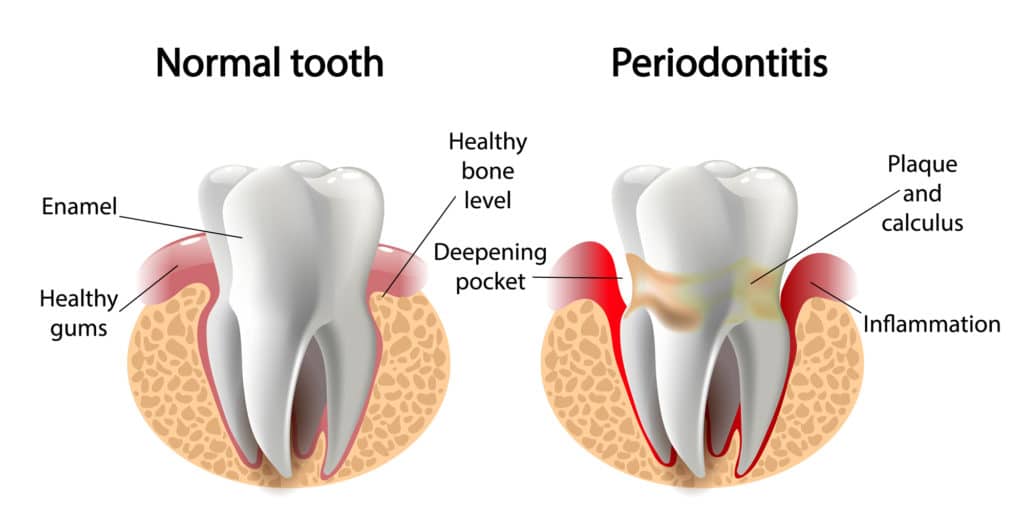
To diagnose periodontitis accurately, a comprehensive evaluation by a dental professional is necessary. This assessment involves reviewing medical history, examining the mouth for plaque and tartar, and measuring the depth of gum pockets. Pockets deeper than 4 mm may indicate the presence of periodontitis, with pockets exceeding 5 mm posing challenges for routine care. Dental X-rays can also aid in identifying bone loss in affected areas.
Treatment options for periodontitis encompass a range of approaches administered by dentists or specialized periodontists. These may include professional cleaning, scaling and root planing, antibiotics, and surgical interventions. Additionally, dentists may prescribe medications to control infection, alleviate discomfort, or facilitate healing.
Effective prevention strategies are within reach through consistent adherence to good oral hygiene practices. Brushing teeth at least twice a day, daily flossing, and integrating mouthwash into routines significantly reduce plaque accumulation.
Awareness of risk factors, such as age, smoking, diet, and genetics, empowers individuals to take proactive steps toward prevention. Regular dental checkups and cleanings play a vital role, alongside smoking cessation and stress reduction techniques.
By embracing these recommendations and prioritizing oral health, individuals can fortify themselves against periodontitis, ensuring a resilient smile and overall well-being.
Causes and Risk Factors for Periodontitis
Beware! Periodontitis, commonly known as gum disease, poses a grave threat to your oral health.
This severe infection ravages the gums and surrounding soft tissues, leaving a trail of destruction. Discover the key causes and risk factors associated with this menacing condition that demands immediate attention.
- Poor Oral Hygiene: Neglecting your oral hygiene is a dangerous path to periodontitis. Failure to remove dental plaque daily allows it to harden into tartar, a breeding ground for gum disease. Shockingly, poor oral hygiene escalates the risk of periodontitis by two to five times compared to good oral hygiene practices.
- Smoking and Tobacco Use: The toxic habit of smoking significantly contributes to severe gum disease in the United States. Smokers face double the risk of gum disease compared to nonsmokers, with the peril amplifying based on the number of cigarettes consumed. Smoking compromises your body’s infection-fighting capabilities, making it harder to combat gum infections.
- Genetics: Unlocking the genetic code reveals its influence on periodontitis. Groundbreaking studies highlight the involvement of at least 65 genes associated with this condition. These genes govern immune function, inflammation, and tissue destruction, weaving a complex genetic tapestry behind periodontal health.
- Stress: Unmasking the invisible enemy, stress disrupts the delicate balance of signals connecting the nervous, endocrine, and immune systems. Prolonged emotional stress triggers excessive release of stress hormones, leading to imbalanced and heightened inflammatory reactions. This cascade of events contributes to the development of periodontal disease.
- Systemic Diseases: Certain systemic diseases, including diabetes or AIDS, and their corresponding medications elevate the risk of periodontitis. Furthermore, this insidious gum disease acts as a potential source of infection, intertwining with various cardiovascular, respiratory, endocrine, and systemic diseases.
By unraveling the causes and risk factors behind periodontitis, you possess the power to shield yourself. Embrace the pillars of good oral hygiene: brush your teeth at least 2 times a day, floss diligently, and prioritize regular dental checkups and cleanings.
Stepping away from smoking, managing stress, and understanding your individual risk factors are additional weapons in your arsenal against periodontitis.
Stages of Periodontal Disease
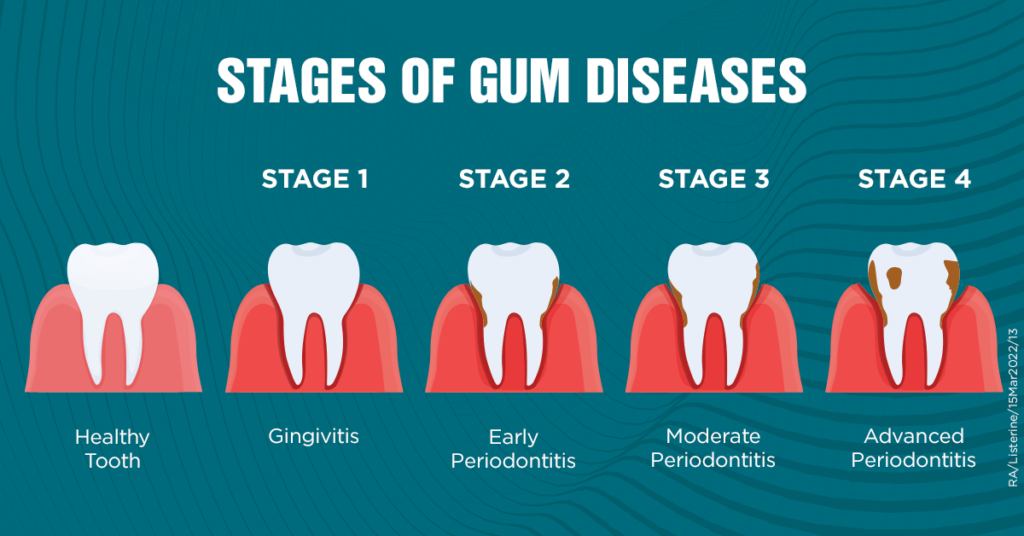
Periodontal disease, a grave infection that ravages the gums and surrounding tissue, demands our immediate attention. Caused by the buildup of bacteria on teeth and gums, this silent predator progresses through five stages, each posing a serious threat to oral health.
Discover the stages below and take action to safeguard your smile.
Stage 1: Gingivitis – A Warning Sign
Gingivitis, the initial stage of gum disease, manifests with red, swollen, and bleeding gums. As plaque accumulates, the risk heightens. The good news? With diligent oral hygiene and regular dental cleanings, gingivitis can be reversed, paving the way for healthier gums.
Stage 2: Early Periodontitis – Nipping It in the Bud
The second stage, early periodontitis, sees the emergence of pockets between teeth and gums, inviting infection and gum recession. Swift intervention through professional cleaning, scaling and root planing, and targeted antibiotics can effectively combat this stage.
Stage 3: Moderate Periodontitis – Deeper Troubles
Moderate periodontitis sets in as pockets deepen and infection threatens the bone. Treatment options, including scaling and root planing, antibiotics, and surgical measures, become essential to halt further damage and preserve oral health.
Stage 4: Advanced Periodontitis – A Battle for Survival
Advanced periodontitis, a critical juncture, witnesses severe bone loss and tooth mobility. Intensive therapies such as scaling and root planing, antibiotics, and surgical procedures, including bone and tissue grafts, become crucial in the fight against this advanced stage.
Stage 5: Refractory Periodontitis – Defying Conventional Measures
In its final stage, refractory periodontitis emerges as an obstinate and rare form of gum disease. Persistent inflammation and bone loss persist despite treatment, demanding more aggressive measures like surgery or laser therapy.
By arming ourselves with knowledge about the five stages of periodontal disease, we hold the power to preempt its destructive impact. Prioritize impeccable oral hygiene, including thorough brushing twice a day, daily flossing, and regular dental visits for checkups and cleanings.
Quitting smoking, managing stress, and recognizing personal risk factors are additional measures that fortify your defense against periodontal disease.
Can Periodontitis be Cured?
Periodontitis, a significant infection affecting gum tissue, warrants careful attention in the realm of oral health. As a condition caused by bacterial accumulation, periodontitis, while not curable, can be effectively managed through comprehensive care and professional interventions.
Addressing periodontitis necessitates tailoring treatment plans to the disease’s severity. In its early stages, non-surgical techniques such as scaling and root planing take precedence, diligently eliminating plaque and tartar from teeth and gums.
Adjunctive antibiotic therapy may be prescribed to aid in infection control. For more advanced cases, surgical procedures like flap surgery or bone and tissue grafts may be warranted to restore oral health.
It is crucial to emphasize that although a definitive cure remains elusive, meticulous care and treatment are key to managing periodontitis.
Upholding good oral hygiene practices, including regular brushing at least twice daily, consistent flossing, and routine dental checkups for cleanings, significantly contribute to the prevention and management of periodontal disease. Equally important are lifestyle modifications such as smoking cessation, stress reduction, and awareness of individual risk factors, which collectively aid in the prevention of periodontitis.
To summarize, while a complete cure for periodontitis remains out of reach, comprehensive care and treatment strategies empower individuals to effectively manage the condition.
Treatment approaches are tailored to the severity of the disease, while embracing exemplary oral hygiene practices and embracing a healthy lifestyle contribute to both prevention and the long-term management of periodontal disease.
Managing Periodontitis at Home
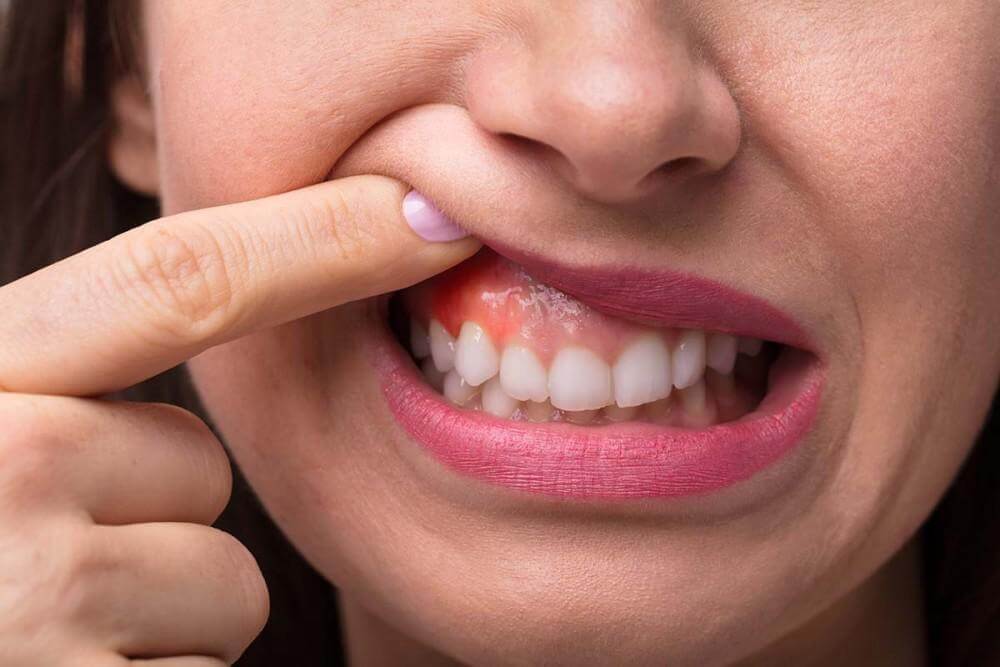
Periodontitis, also known as gum disease, is a serious infection of the gums that damages the soft tissue around teeth. It is caused by bacteria that have been allowed to accumulate on your teeth and gums.
While professional treatment is necessary to manage periodontitis, there are several things you can do at home to help manage the disease.
Oral Hygiene Tips
Good oral hygiene practices can help manage or prevent periodontal disease. Here are some tips to help maintain good oral hygiene:
- Brush your teeth twice a day with a soft-bristled toothbrush and fluoride toothpaste.
- Floss daily to remove plaque and food particles from between your teeth.
- Use an antiseptic mouthwash to help kill bacteria and freshen your breath.
- Brush your tongue to remove bacteria and freshen your breath.
- Replace your toothbrush every three to four months or sooner if the bristles become frayed.
- 6. Visit your dentist regularly for dental checkups and cleanings.
Lifestyle Changes
Certain lifestyle changes can also help manage periodontitis:
- Quit smoking or using tobacco products.
- Eat a healthy diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains.
- Limit sugary and acidic foods and drinks, which can contribute to tooth decay and gum disease.
- Reduce stress levels, which can weaken the immune system and make it harder to fight infections.
- Get enough sleep, which can help boost the immune system and reduce inflammation.
- Exercise regularly, which can help improve overall health and reduce inflammation.
Home Remedies
While professional treatment is necessary to manage periodontitis, there are some home remedies that may help alleviate symptoms:
- Rinse your mouth with warm salt water to help reduce inflammation.
- Use a hydrogen peroxide mouthwash to help kill bacteria.
- Apply a cold compress to your face to help reduce swelling and pain.
- Drink green tea, which contains antioxidants that may help reduce inflammation.
- Use aloe vera gel to help soothe inflamed gums.
- Practice oil pulling with coconut oil to help reduce bacteria in the mouth.
In summary, managing periodontitis at home involves maintaining good oral hygiene practices, making lifestyle changes, and trying home remedies to alleviate symptoms.
While these measures can help manage the disease, it is important to seek professional treatment from a dentist or periodontist to prevent further damage to your gums and teeth.
Editor’s Note: Please contact press@nowthendigital.com if you find any of the content to be inaccurate or outdated.
You’re reading nowthendigital.com — which breaks the news about Uganda, Kenya, Nigeria, South Africa and the rest of the world, day after day. Be sure to check out our homepage for all the latest news, and follow NOW THEN DIGITAL on YouTube, Google, Web Stories, Google News, Medium, LinkedIn, Twitter, Reddit, Pinterest, Linktr, Buy Me a Coffee, Truth Social, and Flipboard to stay in the loop.